The Julian Calendar: A Foundation Of Western Timekeeping
The Julian Calendar: A Foundation of Western Timekeeping
Related Articles: The Julian Calendar: A Foundation of Western Timekeeping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Julian Calendar: A Foundation of Western Timekeeping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Julian Calendar: A Foundation of Western Timekeeping

The Julian calendar, named after Julius Caesar, stands as a cornerstone of Western civilization’s understanding of time. It was a revolutionary system that supplanted the Roman calendar, introducing a more accurate and standardized method for tracking the passage of the year. This article will delve into the history, mechanics, and enduring legacy of the Julian calendar, exploring its significance in shaping our world.
Origins and Development
The Roman calendar prior to Julius Caesar was a chaotic system based on lunar cycles and political decrees. It lacked consistency, leading to discrepancies between the calendar year and the solar year, which created confusion in agricultural practices and religious observances.
In 45 BCE, Julius Caesar, with the assistance of the Alexandrian astronomer Sosigenes, implemented a new calendar system. This calendar, now known as the Julian calendar, aimed to align the calendar year with the solar year, establishing a more accurate system for tracking the seasons.
Key Features of the Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar introduced several key features that revolutionized timekeeping:
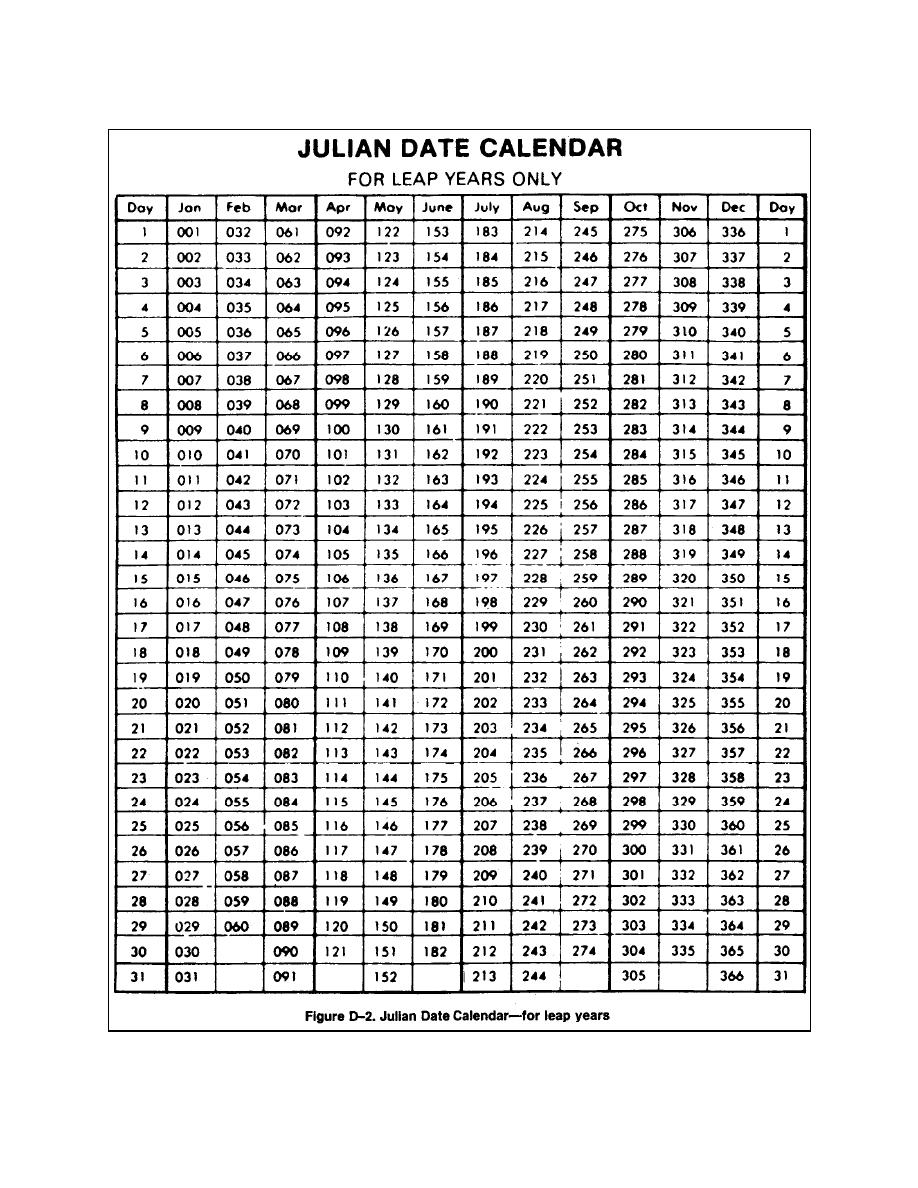
- A 365-day year with a leap year every four years: The calendar year was divided into 12 months, with 365 days. To account for the extra fraction of a day in the solar year, a leap day was added every four years, ensuring the calendar remained synchronized with the solar year.
- Fixed length of months: The Julian calendar standardized the number of days in each month, with the exception of February, which had 29 days in leap years and 28 days in non-leap years.
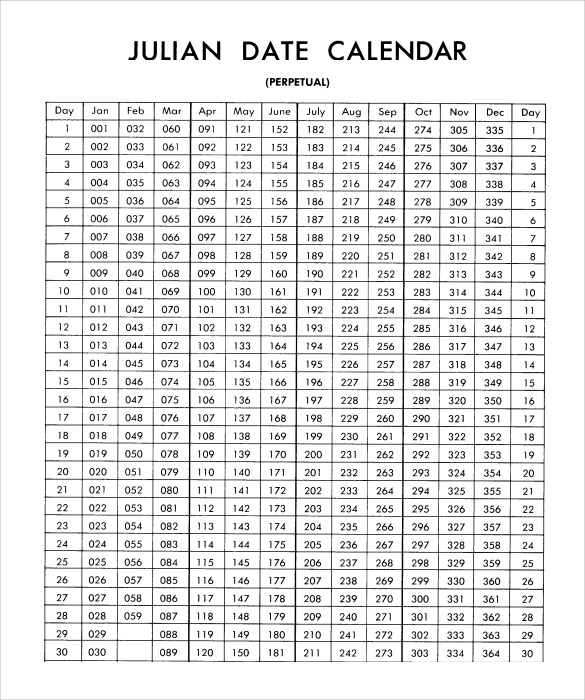
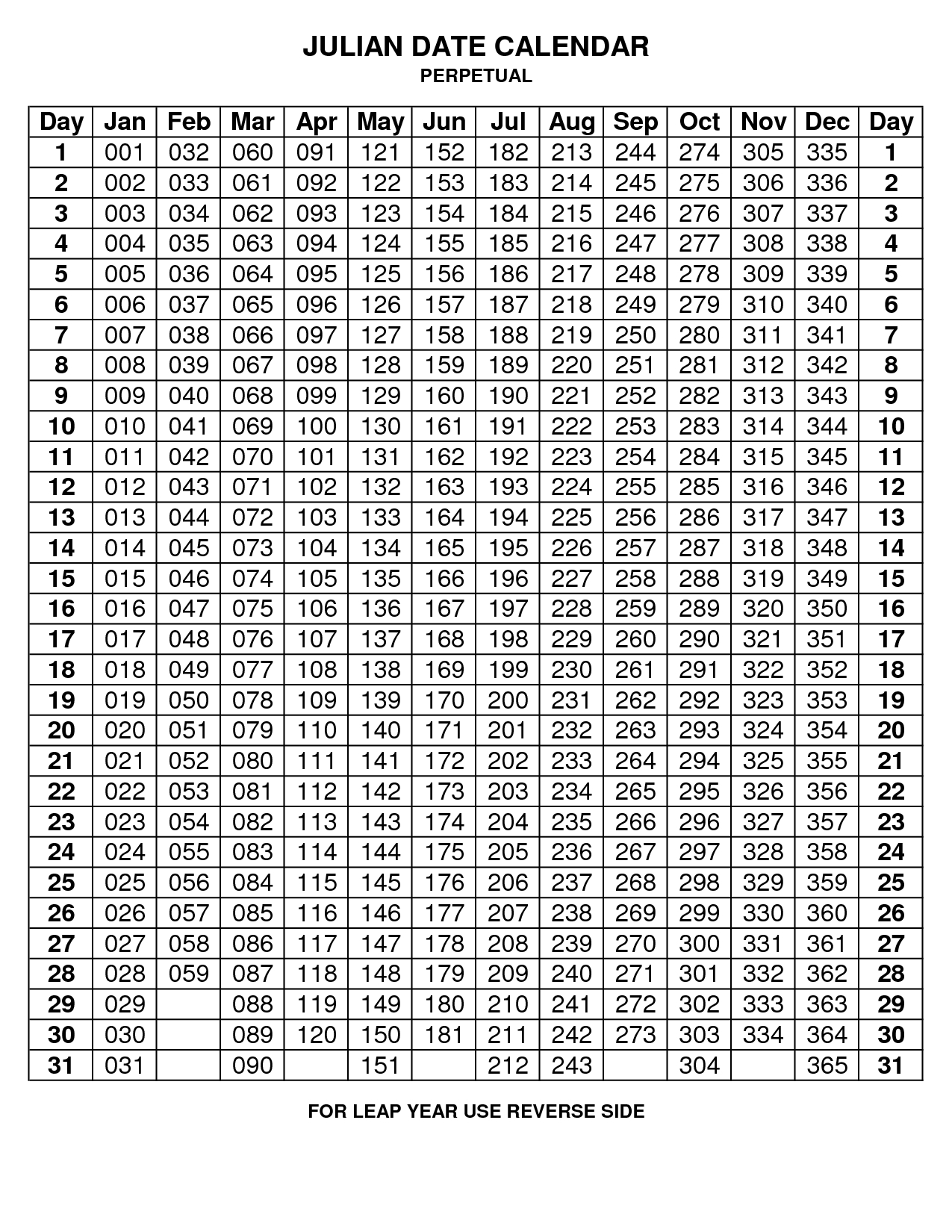
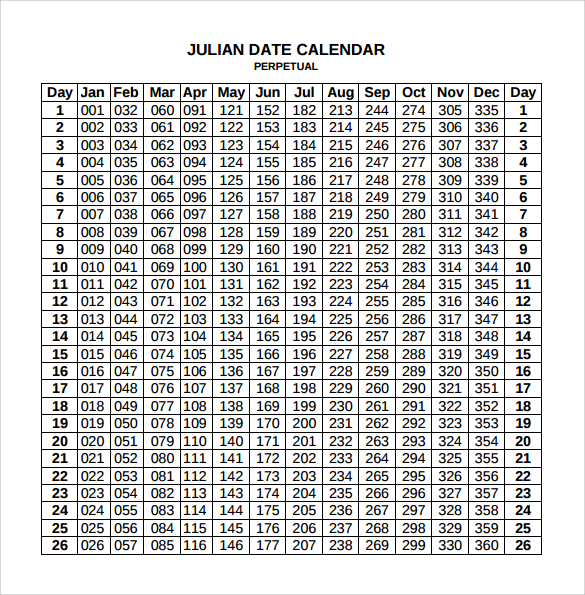
- Introduction of the Julian date: This system, which assigns a numerical date to each day, provided a standardized and universal way to refer to specific dates, facilitating communication and record-keeping.
Impact and Legacy
The Julian calendar’s impact on Western civilization was profound. It provided a standardized and accurate system for timekeeping, which facilitated:
- Agricultural practices: Farmers could plan their planting and harvesting schedules with greater precision, leading to improved agricultural productivity.
- Religious observances: The consistent calendar year allowed for the accurate scheduling of religious festivals and holidays, fostering a sense of order and continuity.
- Commercial activities: Trade and commerce flourished with a reliable system for tracking dates and deadlines.
- Scientific advancements: The Julian calendar’s accuracy and consistency contributed to the development of astronomy and other scientific fields.
The Gregorian Calendar: A Refinement of the Julian System
Despite its groundbreaking nature, the Julian calendar was not without its flaws. The leap year system, while effective, slightly overestimated the length of the solar year. This resulted in a gradual drift between the calendar year and the solar year, with the calendar year gaining approximately 11 minutes every year.
In 1582, Pope Gregory XIII implemented a revised calendar system, known as the Gregorian calendar, to address this discrepancy. The Gregorian calendar adjusted the leap year rules, reducing the number of leap years to ensure a more accurate alignment with the solar year.
The Julian Calendar Today
While the Gregorian calendar is now the dominant system used worldwide, the Julian calendar remains relevant in certain contexts:
- Orthodox Christianity: The Eastern Orthodox Church, along with some other Eastern Christian denominations, continue to use the Julian calendar for religious purposes, including the calculation of Easter.
- Historical research: Historians rely on the Julian calendar to understand and interpret historical events that occurred before the adoption of the Gregorian calendar.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use the Julian date system, a numerical system based on the Julian calendar, to record and communicate astronomical observations.
FAQs
Q: How accurate was the Julian calendar?
A: The Julian calendar was a significant improvement over the Roman calendar, but it slightly overestimated the length of the solar year, leading to a gradual drift between the calendar year and the solar year.
Q: Why was the Gregorian calendar adopted?
A: The Gregorian calendar was adopted to address the drift between the Julian calendar year and the solar year, ensuring a more accurate alignment.
Q: What are the differences between the Julian and Gregorian calendars?
A: The main difference lies in the leap year rules. The Gregorian calendar adjusts the leap year rules, reducing the number of leap years to maintain a more accurate alignment with the solar year.
Q: What are some examples of countries that still use the Julian calendar?
A: While the Gregorian calendar is now the dominant system worldwide, the Julian calendar is still used by the Eastern Orthodox Church for religious purposes.
Tips
- Understanding the Julian calendar’s significance: Recognizing the Julian calendar’s historical context and its impact on Western civilization provides a deeper appreciation for its importance.
- Learning about the Julian date system: Understanding the Julian date system can be helpful for historical research and astronomical observations.
- Exploring the transition to the Gregorian calendar: Researching the adoption of the Gregorian calendar and its impact on different societies provides valuable insights into the evolution of timekeeping.
Conclusion
The Julian calendar stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our enduring quest to understand and track the passage of time. Its influence on Western civilization is undeniable, shaping our understanding of the year, facilitating agricultural practices, and influencing religious observances. While the Gregorian calendar has become the dominant system, the Julian calendar continues to hold significance in historical research, religious practice, and astronomical observation. By appreciating its history and legacy, we gain a deeper understanding of the evolution of timekeeping and its impact on our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Julian Calendar: A Foundation of Western Timekeeping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Academic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The DGF School Calendar
- Mastering Your Week: The Power Of A Weekly To-Do Calendar
- The Enduring Utility Of Whiteboard Calendars: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating Your Academic Journey: A Comprehensive Guide To The UC Clermont Calendar
- Navigating The Path To Success: A Guide To The ELAC Summer 2025 Calendar
- Navigating The Future: A Comprehensive Guide To The 2025 Yearly Calendar
- Navigating Your Academic Journey: A Comprehensive Guide To The George Mason University Calendar
- The Power Of Calendar Subscriptions On IPhone: Streamlining Your Life One Event At A Time
Leave a Reply